The Evolution of Surgical Operating Scissors: From Tradition to Innovation
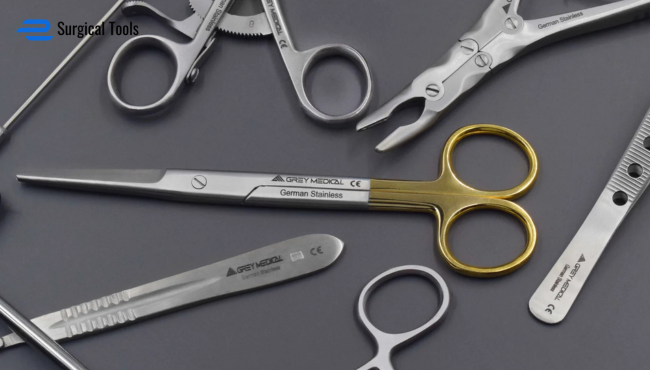
Surgical operating scissors are a vital tool in medicine, essential for procedures demanding precision cutting. From routine surgeries to advanced microsurgical tasks, these instruments ensure accuracy, boost efficiency, and enhance patient safety. The development of surgical operating scissors has progressed through innovations in material science, ergonomic design, and modern technology, revolutionizing how surgeons execute critical procedures with confidence.
The value of precision cutting in surgery is immense. Whether dissecting delicate tissues, trimming sutures, or handling complex operations, the right pair of surgical operating scissors improves efficiency and reduces risks. In the past, medical professionals used basic cutting tools, but today’s scissors offer superior control, durability, and sterility. These qualities lead to better outcomes, making them indispensable in operating rooms worldwide.

With ongoing advancements in surgical tools, modern surgical operating scissors feature high-quality materials like stainless steel alloys, tungsten carbide edges, and laser-sharpened blades for unmatched precision. The emergence of robotic-assisted surgeries and AI-driven innovations marks the future of these instruments. To explore more about surgical tool evolution, visit this detailed resource from the National Institutes of Health. This journey—from humble origins to cutting-edge designs—underscores the enduring importance of surgical operating scissors in today’s medical practices.
Historical Background of Surgical Operating Scissors
Origins of Surgical Scissors in Medicine
The use of cutting tools in medicine traces back to ancient civilizations. Early surgical operating scissors were crafted from bronze, iron, and other metals, featuring basic designs that lacked precision. Ancient Egyptian, Greek, and Roman healers relied on these rudimentary scissors for procedures, depending heavily on their manual dexterity rather than tool sophistication.
By the Middle Ages, surgical instruments advanced, with European surgeons adopting sharper steel blades for greater durability. The Renaissance brought further refinement, introducing scissor designs tailored to specific medical tasks. Still, these handcrafted tools fell short of the ergonomic precision found in modern surgical operating scissors.
The Industrial Revolution and Modernization
The 19th and early 20th centuries transformed surgical instrument development. The introduction of stainless steel in the early 1900s made surgical operating scissors more durable, rust-resistant, and easier to sterilize. Mass production began, ensuring consistent quality across medical settings.
This era also saw the rise of specialized surgical operating scissors, with curved blades for delicate tissue work and serrated edges for improved grip. By the mid-20th century, tungsten carbide inserts were added, enhancing sharpness and wear resistance—key advancements that elevated surgical precision.
Technological Advancements in the 21st Century
Today’s surgical operating scissors reflect remarkable technological progress. Key innovations include:
- Laser-Sharpened Blades: Boost cutting accuracy and minimize tissue damage.
• Ergonomic Designs: Offer better grip and reduce surgeon fatigue.
• Tungsten Carbide and Titanium Coatings: Enhance durability and corrosion resistance.
• Disposable vs. Reusable Scissors: Disposable options ensure sterility, while reusable models offer cost-effective longevity.
• Integration with Robotic Surgery: AI and robotic systems enable unmatched precision in minimally invasive procedures.
Ongoing research promises even smarter surgical operating scissors, potentially adapting to tissue types in real-time. For more on surgical tool evolution, explore this detailed history from the National Institutes of Health.
Types of Surgical Operating Scissors
General-Purpose Surgical Scissors
General-purpose surgical operating scissors are the go-to choice for most medical procedures. These versatile tools cut a variety of materials, from sutures and gauze to delicate tissues. Available with straight or curved blades, they adapt to specific needs—straight blades excel at trimming external materials, while curved blades improve access to internal tissues during surgery. Widely used across specialties, these scissors are prized for their reliability and flexibility in operating rooms everywhere.

Dissecting Scissors
Dissecting surgical operating scissors are engineered for precise tissue cutting in surgical settings. Designed to minimize trauma, they allow surgeons to separate and handle soft tissues with care. Available in blunt and sharp versions, blunt-ended scissors spread tissues apart, while sharp-ended ones make clean cuts. Popular types include Metzenbaum scissors, with long, thin, curved blades for delicate tasks, and Mayo scissors, sturdier for slicing thicker tissues like fascia and muscle.
Microsurgical Scissors
Microsurgical surgical operating scissors cater to highly delicate procedures requiring exceptional precision. Commonly used in ophthalmic, neurological, and vascular surgeries, their ultra-fine tips demand exactness where even minor errors matter. Crafted from premium stainless steel or titanium, they’re lightweight for better control and reduced fatigue during extended operations. With robotic-assisted surgery, these scissors now pair with advanced technology, offering surgeons unparalleled accuracy.
Stainless Steel vs. Tungsten Carbide Scissors
The material of surgical operating scissors greatly affects their performance and lifespan. Stainless steel scissors resist rust and sterilize easily, providing a cost-effective option for medical facilities. Tungsten carbide scissors, however, deliver sharper, longer-lasting blades that rarely need sharpening—perfect for precision-demanding procedures. Though pricier, their durability often outweighs the cost, especially for complex surgeries. For more on surgical materials, see this National Institutes of Health resource.
Disposable vs. Reusable Surgical Scissors
The choice between disposable and reusable surgical operating scissors remains a key discussion in medicine. Disposable scissors, made for single use, guarantee sterility and prevent cross-contamination, making them ideal for emergencies, outpatient care, and high-risk settings. Reusable scissors, requiring thorough sterilization, offer cost savings over time and can be reconditioned. Hospitals favor high-quality reusable options for reliability, but strict protocols are essential to ensure safety and meet health standards.
The Role of Surgical Operating Scissors in Modern Medicine
Importance in General Surgery
Surgical operating scissors are essential in general surgery, enabling precise cutting, dissection, and tissue manipulation with minimal harm to surrounding areas. Surgeons depend on tools like Mayo scissors for dense tissues and Metzenbaum scissors for delicate dissections. With ergonomic designs and sharp blades, these scissors enhance accuracy, lowering the risk of unintended trauma. The success of surgical procedures hinges on selecting high-quality scissors, making their choice a vital step in preparation.
Application in Specialized Surgeries
In specialized fields, surgical operating scissors are tailored for precision to meet unique procedural demands. Examples include:
- Cardiovascular Surgery: Fine-tipped Potts scissors allow accurate incisions in delicate blood vessels, with angled blades improving visibility and control during complex operations.
• Neurosurgery: Microsurgical scissors meet the high precision needs of brain and spinal surgeries, enabling careful tissue dissection with minimal impact on neural structures.
• Ophthalmic Surgery: Ultra-fine Iris and Westcott scissors offer sharpness for eye procedures like cataract removal, their lightweight build supporting precise adjustments without harming sensitive tissues.
• Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery: Specialized scissors aid in skin grafting and cosmetic work, ensuring clean cuts that reduce scarring and support healing.
Impact of Surgical Scissors on Patient Outcomes
The precision and efficiency of surgical operating scissors directly affect patient recovery. Well-crafted, maintained scissors enable accurate procedures, reducing tissue damage and speeding up healing. Conversely, dull or neglected scissors can cause ragged cuts, excessive bleeding, and longer surgeries, risking complications. This underscores the need for top-tier instruments and diligent upkeep. For more on surgical tool standards, see this National Institutes of Health overview.
The Shift Towards Technologically Advanced Surgical Scissors
Advancements in medical technology have transformed surgical operating scissors, boosting precision and usability. Key innovations include:
• Laser-Guided Scissors: Laser systems guide surgeons for pinpoint incisions.
• Electrosurgical Scissors: These cut and coagulate simultaneously, cutting blood loss and enhancing efficiency.
• Robotic-Assisted Scissors: Paired with robotic systems, they refine dexterity and accuracy in minimally invasive surgeries.
As techniques advance, surgical operating scissors remain pivotal for safe, effective procedures.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
FDA Regulations for Surgical Instruments
In the United States, all surgical instruments, including operating scissors, must comply with U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations. The FDA classifies surgical scissors as Class I or Class II medical devices, depending on their intended use. Manufacturers must follow strict Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) under 21 CFR Part 820, ensuring safety, quality, and performance.
Key FDA requirements for surgical operating scissors
- Material Safety: All components must be biocompatible and free from harmful substances.
- Sterility Assurance: Instruments must be sterilizable without degrading in quality.
- Performance Testing: Each instrument must meet sharpness, durability, and precision standards.
ISO and CE Certifications for Medical-Grade Scissors
Apart from FDA regulations, surgical scissors must also adhere to international safety standards. ISO 13485 ensures that medical instruments meet quality management requirements, while ISO 7153-1 specifies the proper stainless steel grades for surgical tools.
Additionally, the CE Marking, mandatory in Europe, indicates that surgical instruments meet European health and safety requirements. Manufacturers must comply with Medical Device Regulation (MDR 2017/745) to distribute their products in European markets.

Hospital Sterilization Protocols to Prevent Infections
To maintain sterility and prevent cross-contamination, hospitals follow strict sterilization procedures for surgical operating scissors:
- Autoclaving: The most common method, using high-pressure steam to kill bacteria and pathogens.
- Chemical Disinfection: Using ethylene oxide (EtO) gas or hydrogen peroxide plasma for delicate instruments.
- Dry Heat Sterilization: Effective for instruments that cannot tolerate moisture.
Sterilization is critical in preventing hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), ensuring that surgical instruments remain safe for reuse.
Proper Handling and Maintenance to Ensure Longevity
Even high-quality surgical scissors require proper care to maintain their precision and durability:
- Routine Inspection: Checking for dull blades, misalignment, or rust.
- Lubrication: Keeping hinge joints smooth to prevent stiffness.
- Proper Storage: Storing scissors in dry, temperature-controlled environments to avoid corrosion.
Regular maintenance ensures that surgical scissors remain functional for multiple procedures while maintaining the highest safety standards.
How to Choose the Right Surgical Operating Scissors
Key Factors to Consider: Blade Type, Material, and Grip Design
Selecting the right surgical operating scissors requires careful attention to key features for precision and ease of use:
Blade Type: Straight blades deliver accurate, clean cuts, while curved blades excel in navigating deep or complex incisions.
• Material: Stainless steel ensures lasting durability, whereas titanium offers a lightweight, corrosion-resistant alternative.
• Grip Design: Ergonomic handles with non-slip grips enhance control and reduce strain during lengthy procedures.
Recommendations Based on Surgical Specialty
Surgical operating scissors vary by specialty, each tailored to specific needs:
- General Surgery: Mayo and Metzenbaum scissors handle tissue dissection with versatility.
• Ophthalmic Surgery: Iris scissors provide precision for delicate eye operations.
• Neurosurgery: Micro scissors enable exact cuts for nerve and brain work.
• Orthopedic Surgery: Heavy-duty shears tackle tough cartilage and ligaments effectively.
Matching scissors to the procedure boosts both accuracy and efficiency.

Comparing Top Brands and Manufacturers
Notable manufacturers of surgical operating scissors include:
B. Braun: Renowned for reliable stainless steel tools.
• Medtronic: Focuses on precision-crafted medical instruments.
• STILLE: Delivers premium scissors for specialized surgeries.
For deeper insights into surgical tool quality, check this National Institutes of Health resource.
Importance of Cost-Effectiveness Without Compromising Quality
While cost matters, opting for high-quality surgical operating scissors avoids frequent replacements and safeguards patients. Low-cost options may dull fast or corrode, risking complications. Hospitals and surgeons should choose FDA-approved and ISO-certified scissors to uphold safety and performance standards.
Challenges and Common Issues with Surgical Scissors
Blade Dullness and Maintenance Challenges
A frequent challenge with surgical operating scissors is blade dullness over time. Repeated use, mishandling, and constant sterilization wear down cutting edges, diminishing precision in surgery. Dull scissors can:
Demand extra force, tiring surgeons’ hands.
• Tear tissues instead of cutting cleanly, slowing recovery.
• Prolong surgery duration, risking poorer patient outcomes.
To address this, hospitals should enforce strict maintenance routines—regular inspections, timely sharpening, and joint lubrication—to prolong the life of surgical operating scissors.
Risk of Contamination and Sterilization Concerns
Proper sterilization of surgical operating scissors is critical to prevent hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). Yet, challenges include:
- Biofilm Formation: Bacteria and debris can build up in hard-to-clean areas.
• Material Degradation: Overuse of autoclaving or chemicals may weaken blades.
• Inconsistent Cleaning: Poor practices risk cross-contamination between uses.
Hospitals must follow CDC and FDA sterilization protocols, using autoclaving, chemical disinfection, or plasma gas methods to ensure hygiene. For more on infection control, see this CDC guideline resource.
Differences in Quality Across Manufacturers
Quality varies widely among surgical operating scissors from different makers. Key distinctions include:
- Material Composition: High-grade stainless steel (like German or Japanese varieties) outlasts cheaper alloys.
• Manufacturing Standards: ISO 13485 and FDA-compliant brands offer reliable quality control.
• Blade Sharpness and Longevity: Superior craftsmanship yields longer-lasting edges.
Surgeons and procurement teams should assess brand reputation, certifications, and feedback to ensure scissors meet medical standards.
How Innovation is Addressing These Issues
Medical technology is enhancing surgical operating scissors with:
- Self-sharpening blades for extended durability.
• Non-stick and antimicrobial coatings to improve sterility.
• Ergonomic handles to ease surgeon strain.
• Smart sensors in robotic-assisted scissors for precise cuts.
These innovations elevate performance and safety, pushing surgical instrument technology forward.
Future Trends in Surgical Operating Scissors
Integration of Nanotechnology for Enhanced Cutting Efficiency
Nanotechnology is transforming surgical operating scissors, elevating their performance in the operating room. Nano-coated blades deliver:
- Sharper edges with greater wear resistance, combating dullness over time.
• Antimicrobial properties to lower infection risks.
• Smoother cuts through reduced friction, enhancing precision.
Hospitals are increasingly adopting these nanotechnology-enhanced surgical operating scissors for improved durability and effectiveness in intricate procedures.
3D-Printed Surgical Scissors: Customization and Rapid Production
3D printing is advancing the medical field by enabling customized surgical operating scissors for specific needs. Key advantages include:
- Quicker production at lower costs than traditional methods.
• Tailored designs to meet unique surgical demands.
• Biodegradable materials for more sustainable healthcare options.
As 3D printing evolves, hospitals could soon produce surgical operating scissors on-site, reducing delays in supply chains.
AI-Driven Cutting Tools for Robotic Surgeries
Artificial intelligence (AI) and robotic systems are redefining precision with surgical operating scissors in modern surgeries. AI-powered scissors:
- Adapt cutting force to tissue resistance automatically.
• Pair with robotic platforms for superior accuracy.
• Minimize human error during delicate operations.
Combined with machine learning, these tools promise better outcomes, especially in minimally invasive procedures. For more on AI in surgery, explore this National Institutes of Health study.
The Shift Toward Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Surgical Instruments
Sustainability is gaining traction in healthcare, influencing surgical operating scissors design. Emerging trends include:
Recyclable stainless steel to lessen environmental harm.
• Biodegradable polymer handles to cut down medical waste.
• Energy-saving sterilization methods to reduce carbon footprints.
With global focus on eco-friendliness, manufacturers are developing greener surgical tools, balancing performance with environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
Surgical operating scissors have evolved dramatically, shifting from basic handcrafted tools to advanced, precision-engineered instruments. Thanks to ongoing progress in material science, nanotechnology, and robotic-assisted surgery, today’s surgical operating scissors offer unmatched efficiency, durability, and safety for medical procedures.
The importance of precision and innovation in surgical tools is undeniable. Surgeons depend on top-quality surgical operating scissors to execute complex tasks accurately. Enhancements in blade sharpness, ergonomic design, and contamination control play a vital role in improving patient outcomes, ensuring safer and more effective surgeries.
Looking forward, the future of surgical operating scissors will be shaped by AI-driven cutting tools, 3D-printed designs, and eco-friendly production methods. As technology advances, these innovations promise heightened precision, efficiency, and sustainability, benefiting both medical professionals and patients. For more on emerging surgical technologies, see this National Institutes of Health overview.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the Best Material for Surgical Operating Scissors?
High-quality stainless steel, like German or Japanese varieties, is best for surgical operating scissors due to its durability and corrosion resistance, with titanium coatings or tungsten carbide inserts enhancing sharpness and longevity.
How Often Should Surgical Scissors Be Sharpened or Replaced?
Surgical operating scissors should be sharpened every 6–12 months with regular use, or replaced if blades become dull, misaligned, or damaged to ensure precise cuts.
Are Disposable Surgical Scissors Better Than Reusable Ones?
Disposable surgical operating scissors offer sterility and convenience for single use, while reusable ones are more cost-effective and eco-friendly with proper sterilization, depending on hospital needs and protocols.
What Are the Safest Sterilization Methods for Surgical Scissors?
Autoclaving, plasma gas sterilization, chemical sterilization with ethylene oxide, and dry heat sterilization are safe and effective for surgical operating scissors, maintaining hygiene and tool lifespan. See this CDC sterilization guide.
How Do I Ensure the Longevity of Surgical Operating Scissors?
Clean surgical operating scissors immediately after use, store them in a dry, sterile environment, inspect and sharpen regularly, and avoid misuse to extend their lifespan.
What Are the Different Types of Surgical Operating Scissors Used in Medical Procedures?
Surgical operating scissors include Mayo for tough tissues, Metzenbaum for delicate dissections, Iris for precision in eye and plastic surgery, Tenotomy for fine microsurgery, and Lister for bandages.
Can Surgical Operating Scissors Be Customized for Specific Procedures?
Yes, surgical operating scissors can be customized with 3D printing and AI design for specific blade sizes, grips, and coatings to suit specialized procedures.
What Is the Difference Between Curved and Straight Surgical Scissors?
Straight surgical scissors provide precise cuts for sutures and materials, while curved ones offer better maneuverability for deep-tissue dissections and complex anatomy.
Are There Eco-Friendly Alternatives for Surgical Operating Scissors?
Yes, recyclable stainless steel, titanium-coated tools, and biodegradable or reusable handles provide eco-friendly options for surgical operating scissors.