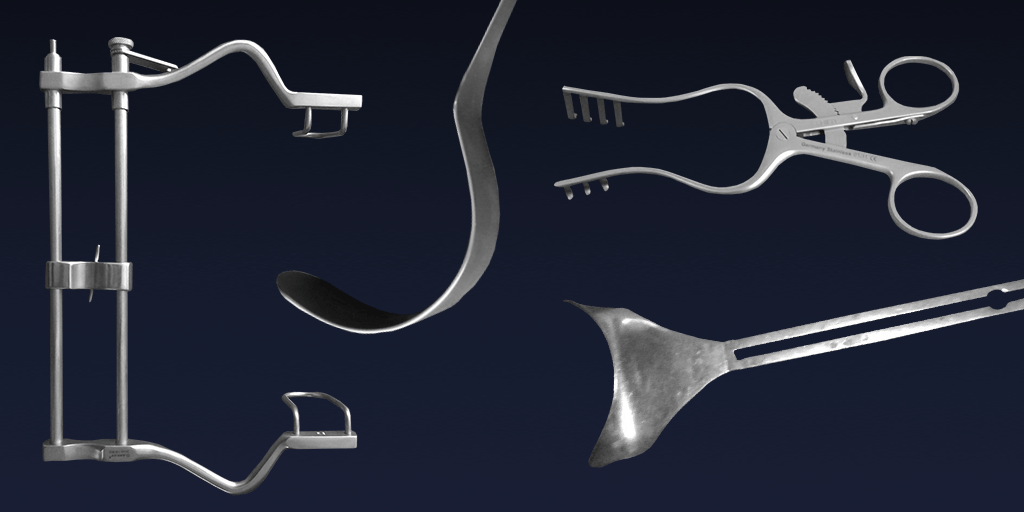
Retractors: Essential Surgical Instruments for Precision and Safety
A retractor is a crucial surgical instrument used to hold back tissues, organs, or skin during medical procedures, providing surgeons with better visibility and access to the surgical site. These instruments are essential in various medical disciplines, including general surgery, orthopedics, neurology, and cardiovascular procedures. Retractors come in multiple forms, such as hand-held retractors operated by assistants and self-retaining retractors designed to stay in place without manual support.
The use of retractors dates back to ancient surgical practices when rudimentary tools were employed to improve access to wounds. Today, advanced materials such as stainless steel and medical-grade plastics ensure durability, sterility, and safety in modern surgical environments. The continuous evolution of retractor technology has led to innovative designs with integrated lighting, suction, and robotic assistance to enhance precision in complex procedures.
For an in-depth understanding of different surgical instruments, including retractors, visit the American College of Surgeons (ACS), a trusted source for surgical guidelines and advancements.
Importance of Retractors in Surgical Procedures
In any surgical operation, precision and visibility are paramount. Retractors play a vital role in:
- Improving surgical access – By holding back tissues or organs, retractors expose deeper areas of the body that would otherwise be difficult to reach.
- Minimizing tissue damage – Properly designed retractors distribute force evenly, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues.
- Enhancing procedural efficiency – A well-positioned retractor allows surgeons to work swiftly and accurately, reducing operation time.
- Supporting various surgical specialties – From minor incisions to major surgeries, retractors are indispensable in procedures like spinal surgery, abdominal surgery, and orthopedic interventions.
With retractors tailored to different medical applications, surgeons can perform intricate procedures with enhanced accuracy, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
How Retractors Contribute to Patient Safety and Surgical Efficiency
Patient safety is a top priority in any medical procedure, and retractors play a key role in ensuring optimal surgical conditions. When used correctly, they:
- Reduce the risk of accidental injury – By holding tissues securely in place, retractors prevent unintended cuts or punctures.
- Enhance visualization – Clear visibility of the surgical field helps surgeons make precise incisions and avoid complications.
- Maintain a sterile environment – Self-retaining retractors reduce the need for additional hands in the surgical field, lowering contamination risks.
- Shorten surgery duration – A well-positioned retractor helps surgeons work efficiently, minimizing the time a patient spends under anesthesia, which can reduce complications and improve recovery times.
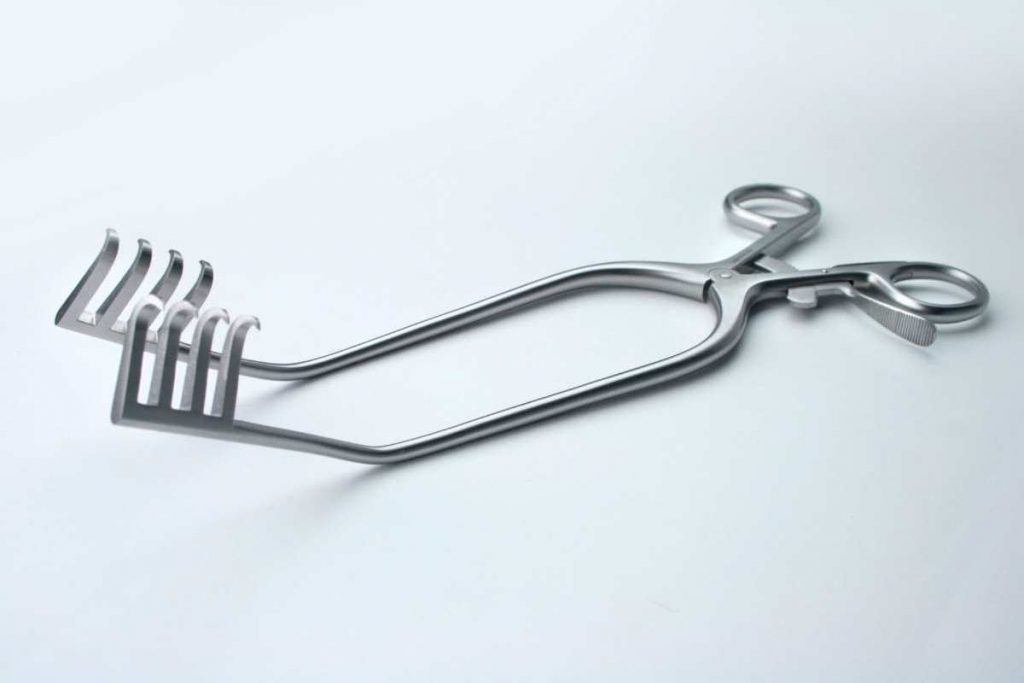
As the demand for minimally invasive procedures increases, the role of retractors continues to evolve. Modern innovations, such as robotic-assisted retractor systems and AI-driven surgical tools, are further refining the precision and safety of surgical interventions.
In the following sections, we will explore different types of retractors, their applications in surgery, and how they contribute to advancing medical practices across the USA.
1. What Are Retractors?
Definition and Purpose in Surgical and Medical Applications
A retractor is a surgical instrument used to hold back tissues, organs, or incisions during medical procedures. It provides better visibility and access to the surgical site, ensuring precision and efficiency. Retractors are essential in various specialties, including general surgery, orthopedics, neurosurgery, and cardiovascular procedures.
How Retractors Have Evolved in Modern Medicine
Retractors have significantly advanced from their rudimentary forms in early surgical history. Initially made from bone or simple metals, modern retractors are now crafted from high-grade stainless steel and medical-grade plastics. The introduction of self-retaining retractors and specialized retractors has enhanced surgical accuracy, reduced manual effort, and improved patient safety.
Key Functions in Different Types of Surgeries
- Tissue Retraction – Holding soft tissues or skin away from the incision site.
- Organ Retraction – Securing internal organs to allow better access to the surgical field.
- Wound Exposure – Keeping incisions open for prolonged procedures.
- Minimizing Tissue Damage – Preventing accidental tissue trauma by stabilizing surrounding areas.
2. Types of Retractors Used in the USA
Hand-Held Retractors
Hand-held retractors are manually positioned by surgeons or assistants. They are commonly used in minor to moderate surgical procedures.
Examples of Hand-Held Retractors
- Army-Navy Retractor – Used in general surgery for exposing superficial or deep tissues.
- Senn Retractor – Designed for delicate procedures like plastic surgery and dermatology.
- Richardson Retractor – Common in abdominal surgeries, providing deep tissue exposure.
Self-Retaining Retractors
Self-retaining retractors are equipped with a locking mechanism, allowing them to remain in place without manual assistance. These retractors improve surgical efficiency and reduce hand fatigue for medical professionals.

Examples of Self-Retaining Retractors
- Balfour Retractor – Used in abdominal and pelvic surgeries for holding large incisions open.
- Weitlaner Retractor – Features pronged tips and is often used in orthopedic and spinal surgeries.
- Gelpi Retractor – Common in neurosurgery and small incision procedures due to its sharp outward-bending tips.
Specialty Retractors
Specialty retractors are designed for specific medical fields and procedures. These instruments cater to the unique needs of various surgical disciplines.
Examples of Specialty Retractors
- Rib Spreaders (Thoracic Retractors) – Used in cardiothoracic surgery for opening the rib cage.
- Ophthalmic Retractors – Delicate instruments used in eye surgeries for precision.
- Neurosurgical Retractors – Designed to provide access to the brain and spinal cord while minimizing tissue disruption.
Disposable vs. Reusable Retractors
Pros and Cons of Disposable Retractors
Advantages:
- Sterile and ready for use, reducing infection risks.
- Convenient for emergency and single-use procedures.
- Eliminates sterilization costs and maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- Higher long-term costs due to repeated purchases.
- Environmental concerns related to medical waste.
Pros and Cons of Reusable Retractors
Advantages:
- Cost-effective in the long run.
- Durable and reliable for multiple procedures.
- Environmentally friendly compared to disposable options.
Disadvantages:
- Requires strict sterilization to prevent contamination.
- Initial investment is higher compared to disposable retractors.
For further information on medical instrument regulations, visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA).
3. Common Surgical Applications of Retractors in the USA
Retractors play a crucial role in various medical specialties, enhancing visibility, improving precision, and minimizing complications. Below are some of the most common surgical applications of retractors in the USA:
General Surgery
- Used in abdominal procedures such as appendectomies, hernia repairs, and bowel resections.
- Richardson and Deaver retractors help expose deep tissue layers.
- Balfour retractors assist in keeping large incisions open.
Orthopedic and Spinal Procedures
- Weitlaner and Gelpi retractors are frequently used in spinal surgeries.
- Hohmann retractors aid in joint surgeries like hip and knee replacements.
- Rib spreaders assist in thoracic surgeries related to the spine.
Cardiovascular Surgery
- Rib spreaders allow access to the heart and lungs during open-heart surgery.
- Finochietto retractors are commonly used in thoracic procedures.
- Vessel retractors help manage blood vessels during bypass surgeries.
Neurosurgery and Ophthalmic Procedures
- Cerebellar retractors stabilize the brain during delicate procedures.
- Eyelid retractors assist in ophthalmic surgeries, such as cataract removal.
- Self-retaining brain retractors minimize trauma during neurosurgical interventions.

Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Senn and skin retractors help expose delicate facial structures.
- Lip and nasal retractors are used in rhinoplasty and lip augmentation.
- Hand-held micro retractors assist in precision-based reconstructive work.
4. Materials and Manufacturing Standards for Retractors in the USA
The material composition and regulatory compliance of retractors are essential for ensuring their safety, durability, and efficiency in medical settings.
Stainless Steel vs. Plastic Retractors
|
Feature |
Stainless Steel Retractors |
Plastic Retractors |
|
Durability |
Highly durable and reusable |
Designed for single-use |
|
Sterilization |
Autoclavable and resistant to corrosion |
Usually pre-sterilized, not reusable |
|
Cost |
Higher initial cost, but long-term savings |
Lower upfront cost, but repeated purchases add up |
|
Application |
Used in major surgeries requiring precision |
Ideal for emergency or disposable use to prevent cross-contamination |
FDA Regulations on Medical Instruments
The U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval and regulation of medical instruments, ensuring that retractors meet high safety and performance standards. The FDA classifies surgical instruments based on risk level:
- Class I: Low-risk devices (e.g., manual retractors).
- Class II: Moderate-risk devices requiring performance standards (e.g., self-retaining retractors).
- Class III: High-risk instruments needing pre-market approval.
To learn more, visit the FDA Medical Device Regulations.
American Medical Association (AMA) Guidelines on Surgical Tools
The American Medical Association (AMA) provides best practices for the proper handling, sterilization, and maintenance of surgical instruments, ensuring patient safety and procedural efficiency.
5. How to Choose the Right Retractor for Surgery
Selecting the right retractor is crucial for ensuring surgical efficiency, patient safety, and surgeon comfort. Various factors determine the most suitable retractor for a procedure, including size, material, and specialty-specific requirements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Retractor
Size & Shape
- Large retractors (e.g., Balfour retractors) are ideal for deep cavity surgeries.
- Small retractors (e.g., Senn retractors) are useful for minor and delicate procedures.
- The blade width should align with the incision size for optimal exposure.
Type of Retractor
- Hand-held retractors: Best for procedures where an assistant can hold the instrument.
- Self-retaining retractors: Ideal for surgeries requiring prolonged exposure without manual support.
- Specialty retractors: Designed for niche applications (e.g., ophthalmic, neurosurgical, or cardiovascular procedures).
Material
- Stainless Steel: Preferred for durability and reusability.
- Plastic: Best for disposable use, reducing infection risk in emergency settings.
Ergonomic Design
- Lightweight retractors reduce hand fatigue for surgeons.
- Non-slip handles ensure precision and control during surgery.
- Properly balanced instruments improve efficiency and reduce muscle strain.
Recommendations for Different Surgical Specialties
|
Specialty |
Recommended Retractors |
|
General Surgery |
Richardson, Deaver, and Army-Navy retractors |
|
Orthopedic Surgery |
Hohmann, Gelpi, and Weitlaner retractors |
|
Neurosurgery |
Leyla self-retaining and cerebellar retractors |
|
Cardiovascular Surgery |
Finochietto rib spreaders and vessel retractors |
|
Plastic Surgery |
Senn, skin, and micro retractors |
|
Ophthalmic Surgery |
Desmarres and Barraquer eyelid retractors |
6. Proper Sterilization and Maintenance of Retractors
Maintaining surgical retractors is essential for infection control, prolonging instrument lifespan, and ensuring patient safety. Hospitals and surgical centers must follow strict sterilization protocols to prevent contamination.
Best Practices for Cleaning and Sterilization in Hospitals
Pre-Cleaning
- Immediately rinse retractors after use to remove blood and tissue debris.
- Use enzymatic detergents to break down organic matter.
Ultrasonic Cleaning
- Submerge instruments in an ultrasonic cleaner to remove microscopic contaminants.
- Ensure proper temperature and detergent concentration for effectiveness.
Autoclaving & Sterilization
- Use a steam autoclave for stainless steel retractors.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for temperature and pressure settings.
- For plastic retractors, use ethylene oxide (EtO) gas sterilization or gamma radiation.

CDC and FDA Guidelines for Infection Control
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the FDA provide stringent guidelines on sterilization techniques for surgical instruments. Some key recommendations include:
- Regular validation of sterilization equipment.
- Using sterilization indicators to confirm effectiveness.
- Proper storage in sterile environments to prevent contamination.
For more details, refer to the CDC Infection Control Guidelines.
Preventing Cross-Contamination with Proper Handling
- Always wear sterile gloves when handling retractors post-sterilization.
- Store retractors in sterilized trays or sealed pouches until use.
- Avoid mixing reusable and disposable retractors in the same set.
- Implement routine inspections to check for instrument wear and tear.
7. Innovations and Technological Advancements in Retractors
As surgical procedures become more advanced, retractor technology continues to evolve to enhance precision, efficiency, and patient outcomes. Recent innovations include retractors with integrated lighting, suction features, and robotic-assisted designs.
Retractors with Integrated Lighting and Suction Features
Illuminated Retractors:
- Built-in LED lighting improves visibility in deep surgical cavities.
- Reduces the need for external lighting sources, enhancing surgeon efficiency.
- Example: Fiber-optic retractors used in minimally invasive surgeries.
Retractors with Suction Capabilities:
- Help clear fluids and blood from the surgical site.
- Improve surgeon visibility without additional suction tools.
- Example: Poole Suction Retractor, commonly used in abdominal surgeries.
Robotic-Assisted Retractors for Precision Surgeries
- Used in minimally invasive and complex procedures like robotic-assisted laparoscopy.
- Provide superior stability and adjustability compared to manually operated retractors.
- Example: Da Vinci Surgical System, which integrates robotic retractors for delicate procedures.
The Future of AI-Powered Surgical Tools
- AI-driven retractors could adjust tension dynamically based on real-time tissue feedback.
- Smart retractors may reduce tissue trauma by optimizing pressure and positioning.
- AI-assisted robotic systems could enhance surgeon precision and control.
8. Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers of Retractors in the USA
High-quality surgical retractors are essential for maintaining medical standards and ensuring patient safety. Many reputable manufacturers and suppliers in the USA produce top-tier surgical instruments.
Top Medical Instrument Manufacturers in the USA
- Medtronic – Offers a wide range of surgical tools, including specialty retractors.
- Integra LifeSciences – Specializes in neurosurgical and orthopedic retractors.
- Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD) – Supplies high-quality general surgery retractors.
- Johnson & Johnson (Ethicon) – Innovates in laparoscopic and minimally invasive surgical instruments.
- Stryker Corporation – Produces orthopedic retractors and surgical instrument kits.
Where to Buy High-Quality Surgical Retractors
- Authorized Medical Suppliers: Henry Schein, McKesson, Cardinal Health.
- Online Medical Equipment Retailers: Medline, AliMed, and Avante Health Solutions.
- Direct from Manufacturers: Many manufacturers offer direct sales or distributor networks.
Price Ranges and Factors Affecting Cost
The price of surgical retractors depends on factors such as material, design, and intended use.
|
Type of Retractor |
Price Range (USD) |
|
Basic Hand-Held Retractors |
$30 - $150 |
|
Self-Retaining Retractors |
$200 - $1,000+ |
|
Specialty Retractors (Neurosurgical, Cardiovascular) |
$500 - $5,000 |
|
Robotic-Assisted Retractors |
$10,000+ |
Factors Affecting Cost
- Material: Stainless steel is more expensive than plastic but lasts longer.
- Brand & Manufacturer: Well-known brands often command higher prices.
- Sterilization Compatibility: Reusable retractors cost more due to higher-quality materials.
- Technology Integration: Advanced features like lighting and suction increase costs
9. Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Ensuring compliance with regulatory and safety standards is critical for maintaining the quality, safety, and effectiveness of surgical retractors used in the USA. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and various medical organizations establish guidelines to regulate surgical tools and their use.
FDA Approval Process for Medical Instruments
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval and regulation of medical devices, including surgical retractors, under its Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH).
Key Steps in the FDA Approval Process for Retractors
Device Classification
- Class I: Low-risk devices (e.g., basic hand-held retractors).
- Class II: Moderate-risk devices requiring special controls (e.g., self-retaining retractors).
- Class III: High-risk devices that require Pre-Market Approval (PMA) (e.g., robotic-assisted retractors).
Premarket Notification (510k) or Premarket Approval (PMA)
- Most retractors fall under Class I or II and require a 510(k) submission, proving they are substantially equivalent to existing devices.
- Advanced retractors with new technology may require PMA approval, a more rigorous process.
Quality System Regulation (QSR) Compliance
- Manufacturers must follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure product consistency and safety.
Post-Market Surveillance
- The FDA monitors surgical instruments for adverse events and recalls to maintain safety.
OSHA Regulations on Surgical Tool Handling
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establishes regulations to protect healthcare workers and patients from hazards associated with surgical tools, including retractors.
OSHA’s Key Surgical Tool Regulations
Bloodborne Pathogens Standard
- Ensures proper handling, sterilization, and disposal of surgical instruments.
- Requires the use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) when handling contaminated tools.
Sharps Safety Regulations
- Encourages the use of blunt-tip retractors in procedures where applicable to reduce accidental injuries.
Ergonomic Safety Standards
- Emphasizes the design of ergonomic surgical tools to minimize strain on surgeons during long procedures.
Best Practices in US Hospitals and Surgical Centers
- Sterile Processing Departments (SPD) ensure proper sterilization and maintenance of retractors.
- Surgical teams follow standardized protocols for handling, storage, and disposal.
- Routine audits and training programs ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Conclusion
Retractors play a vital role in modern surgical procedures across the USA, ensuring better visibility, precision, and accessibility for surgeons. From hand-held and self-retaining retractors to specialized and robotic-assisted models, these essential surgical tools have evolved significantly to meet the demands of various medical specialties.
Choosing the right retractor is crucial for successful surgical outcomes. Factors such as material, ergonomic design, and regulatory compliance should always be considered. High-quality retractors, whether reusable stainless steel or disposable models, contribute to patient safety and efficiency in the operating room.
Looking ahead, the future of surgical retractors lies in technological advancements, such as AI-powered tools, retractors with integrated lighting, and robotic-assisted devices. As innovation continues, the industry will see more precise, efficient, and surgeon-friendly solutions, ultimately enhancing patient care and surgical success rates.
For surgeons and healthcare facilities, staying updated on FDA regulations, OSHA standards, and sterilization guidelines ensures compliance and safety in medical practice. By selecting high-quality retractors from reputable manufacturers, hospitals can maintain excellence in surgical procedures and deliver optimal patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Retractors
What is a retractor in surgery?
A retractor is a surgical instrument used to hold back tissues, organs, or incisions to provide better visibility and access for the surgeon during a procedure.
What are the main types of retractors used in the USA?
The main types include hand-held retractors, self-retaining retractors, specialty retractors, and disposable vs. reusable retractors.
What is the difference between hand-held and self-retaining retractors?
Hand-held retractors require an assistant to hold them in place, while self-retaining retractors have locking mechanisms that keep them in position without manual support.
Which surgical specialties commonly use retractors?
Retractors are used in various fields such as general surgery, orthopedic and spinal procedures, cardiovascular surgery, neurosurgery, ophthalmic surgery, and plastic & reconstructive surgery.
What materials are commonly used to manufacture surgical retractors?
Surgical retractors are typically made from stainless steel for durability and sterilization purposes, though plastic retractors are also used for disposable applications.
Are retractors regulated by the FDA?
Yes, all surgical instruments, including retractors, must meet FDA regulations and undergo rigorous safety testing before being approved for use in medical facilities.
How should retractors be sterilized?
Retractors should be cleaned using hospital-grade disinfectants and sterilized through autoclaving, chemical sterilization, or high-temperature steam processing, following CDC and FDA guidelines to prevent infections.
What are some of the top manufacturers of surgical retractors in the USA?
Some leading medical instrument manufacturers include Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson, Becton Dickinson, Stryker, and Integra LifeSciences, among others.
What innovations are improving retractors today?
Modern retractors now include integrated lighting, suction capabilities, and robotic assistance to improve precision and surgical outcomes. AI-powered tools are also emerging in the field.
Where can I buy high-quality surgical retractors in the USA?
High-quality retractors can be purchased from medical supply companies, surgical equipment manufacturers, and specialized online marketplaces that cater to hospitals and healthcare providers.